Child Mental Health Awareness
Raising awareness about children’s mental health is vital in today’s world. Children, like adults, experience a wide range of emotions, and understanding their mental health is key to fostering their well-being. Early detection and intervention can help prevent potential issues from escalating into more serious conditions. Being aware of mental health challenges children face encourages parents, educators, and society to create a supportive environment where kids can thrive emotionally and psychologically.
Signs of Anxiety in Children
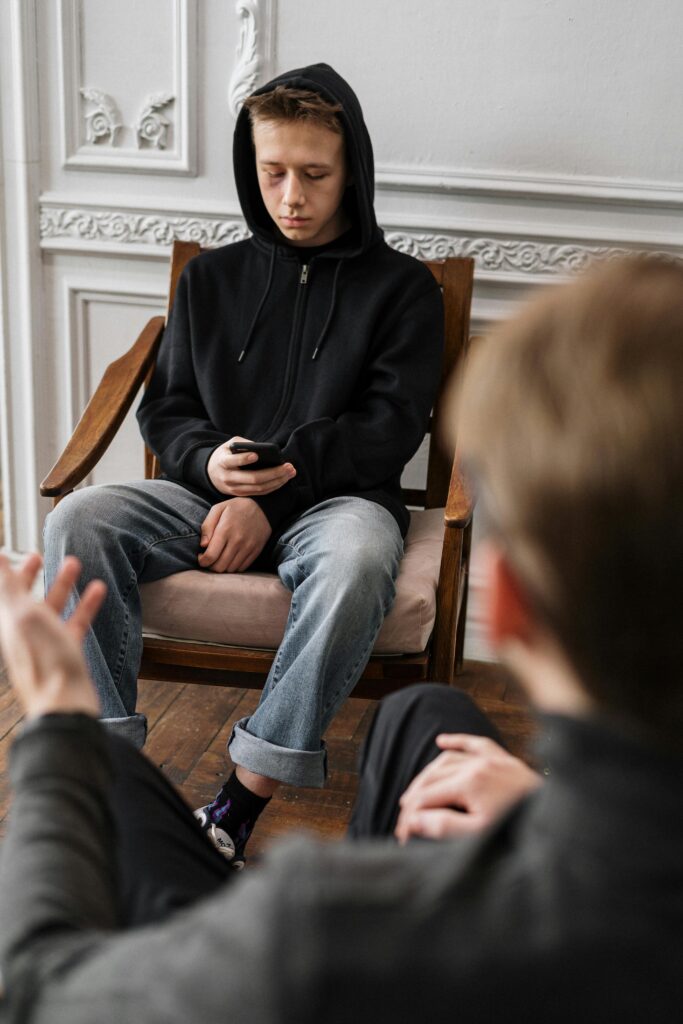
Anxiety is one of the most common mental health issues in children, but it can be difficult to spot as it may manifest in ways that are mistaken for normal childhood behavior. Some signs of anxiety in children include persistent worrying, difficulty concentrating, irritability, sleep disturbances, and physical symptoms such as headaches or stomachaches. Additionally, anxious children may avoid social situations or specific activities that trigger fear. Recognizing these signs early allows parents and caregivers to offer the support needed to help alleviate anxiety and build coping strategies.
Emotional Regulation for Kids

Emotional regulation is a critical skill for children to develop as it helps them manage their feelings and respond to situations in healthy ways. Teaching kids how to identify, understand, and manage their emotions enables them to cope with stress and frustration more effectively. Parents can model emotional regulation by demonstrating calm responses during stressful situations, practicing mindfulness exercises with their children, and encouraging open discussions about feelings. Emotionally regulated children are better equipped to navigate social relationships and school environments with greater ease.
Impact of Trauma on Child Development
Trauma, whether from an isolated event or chronic exposure to stressful experiences, can have a profound effect on a child’s development. Children who have experienced trauma may struggle with trust, emotional regulation, and forming healthy relationships. The long-term effects of trauma can manifest as anxiety, depression, behavioral issues, and difficulty in school. It’s essential to provide trauma-informed care that focuses on creating a safe and supportive environment, while also offering therapeutic interventions that help children process their experiences in a healthy way.

Childhood Depression Symptoms
Depression in children is often overlooked or mistaken for typical moodiness, but it’s a serious condition that requires attention. Symptoms of childhood depression can include persistent sadness, withdrawal from activities once enjoyed, changes in eating or sleeping patterns, irritability, and low energy. In some cases, children may express feelings of worthlessness or hopelessness, or even have thoughts of self-harm. Early identification and treatment of depression, whether through therapy, lifestyle changes, or medication, can significantly improve a child’s quality of life and prevent more severe issues in adulthood.
Conclusion
Child mental health is an integral part of overall well-being, and recognizing the signs of anxiety, depression, and trauma early on can help mitigate their long-term impact. Emotional regulation skills and awareness of these mental health challenges allow parents and caregivers to support children in developing resilience and coping strategies. Through early interventions and a focus on mental health, we can ensure children grow up feeling emotionally secure, mentally strong, and well-supported.